BLOG | MAP technology
How Does Modified Atmosphere Packaging Protect Food?

Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) is a process that can change the way both food consumers and suppliers look at fresh food.
Eating healthy is good for everyone, however, the reduced shelf life of (most) fresh products could easily serve as a barrier for people trying to change their eating habits. This problem goes the other way too. Food suppliers can find themselves with a small time window available to sell fresh produce, meat, healthy snacks, etc., and end up short on revenue because of that.
MAP packaging involves a particular set of tools and resources that enable food sellers and vendors to package food in a way to extend its shelf life and maintains its healthy characteristics.
How Does Modified
Atmosphere Packaging Work?
MAP can work through a different set of machines and specific processes, but the central idea remains the same. As the full name suggests, the process consists of altering (or controlling) the atmosphere of the food package and, consequently, the atmosphere that surrounds the product. This can be done in one of two ways. The first consists of eliminating unwanted gasses present in the former packaging and replacing them with new gasses, which is known as active modified atmosphere packaging.
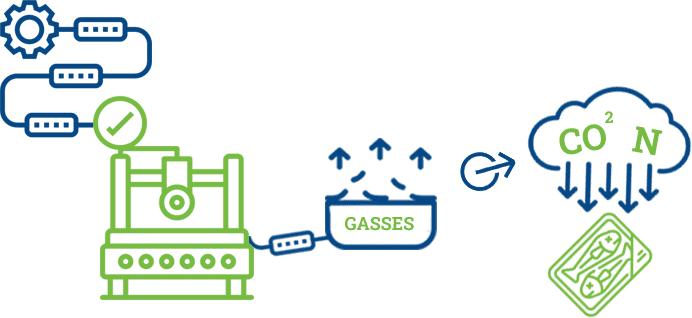
And the second is where you utilize a special type of film to package your product, and this film will naturally entice the formation of a new atmosphere surrounding the product, which is known as passive modified atmosphere packaging.


Naturally, both ways provide new atmospheres that are more beneficial to the product’s shelf life than the previous, since they are extremely efficient in combating the natural processes responsible for making healthy food perish so quickly.
What Type of Food Can Modified Atmosphere Packaging Protect?
If you’ve ever been into a grocery store, chances are you’ve seen examples of MAP packages. MAP packaging commonly surrounds fruits and vegetables, but many other types of food can benefit from this anti-spoiling method. The main ones are:

Meat
If you leave meat outside of the fridge, it will spoil sooner than any other type of food mentioned here. That’s because meat is extremely sensitive to bacteria growth. In MAP for meat, the oxygen inside of the package is replaced by a mixture of carbon dioxide (CO²), nitrogen, and a bit of carbon monoxide. This mixture effectively inhibits bacteria (and other microorganisms) growth. It also avoids oxidation and helps to preserve flavor.

Coffee
Coffee aficionados know how important it is to preserve the beans’ flavor and smell. For that, food suppliers often utilize One-Way Valves, a MAP tool that enables the packaging to release carbon dioxide – commonly released by roasted coffee beans – while not letting any oxygen, or other ambient gasses, get in. This allows for the coffee to maintain freshness for a considerable period.

Fruits & Vegetables
Grapes, apples, carrots, and lettuce all have one thing in common: they’re extremely sensitive to oxidation. The shelf life of produce in general is heavily assisted by the modified atmosphere packaging process. Commonly, fruits and vegetables are packaged through barrier packaging films and gas flush. This means oxygen is replaced by nitrogen and the product is sealed with a special film after.

Snacks
Some snacks may not be as healthy as the other foods mentioned, but MAP is still very successful in keeping them fresh. Also, with the use of barrier packaging films, the number of additives and preservatives in snacks can be significantly reduced, and your health won’t suffer such a strong blow if you eat them.
How Does Modified Atmosphere Packaging Protect Food?
The perishing of food is caused by natural processes that are sped up by an unaltered atmosphere, turning fresh food non-consumable faster than most people would prefer. Here are the main processes combated by MAP to extend product shelf life:
Oxidation
Although the level of oxygen in our atmosphere isn’t as high as many would think (only 21%), it’s enough to stimulate microorganism growth that can cause spoilage. In the case of foods with fats, the unwanted process will become even more noticeable, since the carbon compounds lipids produce during spoilage are stronger, leading to very undesirable tastes and flavors.
Also, materials often utilized in MAP packagings such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride are known to decrease permeability to both oxygen and external moisture.
Moisture
Another propeller of microorganism growth in food is excessive moisture and humidity. Moisture is often responsible for mold growth too, something you’ve certainly seen in expired bread or perishing fruits. MAP manages to inhibit mold growth by inserting carbon dioxide in the packages, which slows down the process considerably.
The special packaging also isolates fresh food from external humidity and moisture that could accelerate the spoilage process.
Light and Temperature
Through gas replacement and special film packaging, MAP also can decrease the product’s sensibility to light and temperature. On many occasions, heat and excess light are responsible for food spoilage. Light does that through a process called photodegradation, which affects the pigments, proteins, and vitamins of food, resulting in color and flavor changes.
And high temperatures are responsible for speeding up both enzyme actions and oxidation, as well as making fresh produce lose (important) moisture, making the product gain a dry, undesirable aspect.
Let MAPtech Help You?
MAPtech has all the tools you need to implement modified atmosphere packaging into your business’ logistics and optimize your time, stock and revenue.
To learn more about the resources we can offer, feel free to check out some of our available equipment and some of the materials we work with.
Recent Posts

What is MAP Packaging?
What is Modified Atmosphere Packaging? Technology has evolved enough to

MAPtech Packaging is Certified by the Women’s Business Enterprise National Council
Maptech Packaging is proud to announce our national certification as

The Freshness Facts of Modified Atmosphere Packaging
Why Modified Atmosphere Packaging? Today’s families are rejecting fast food meals

Jennifer Pfuhl Takes the Helm at Maptech Packaging, Inc.
Hilton Head Island, SC, November 1, 2017 – Maptech Packaging,
Work With The Industry Leader in Extended Shelf Life
Connect with one of our expert team members about how we can bring your packaging dreams to life.



